Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
→ Article about running any deep learning model with ONNX Runtime such as YOLO, Faster R-CNN, ResNet, and more.
There are different libraries and frameworks for training and running different deep learning models. You can run YOLO object detection models with Ultralytics, or for image classification models, you can use Keras or PyTorch.
Using ONNX Runtime, you can run any deep learning model. Also, ONNX Runtime supports running models on both GPU and CPU.
In this article, I will show you how to run YOLO object detection, Faster R-CNN object detection, and ResNet image classification models using only ONNX Runtime.
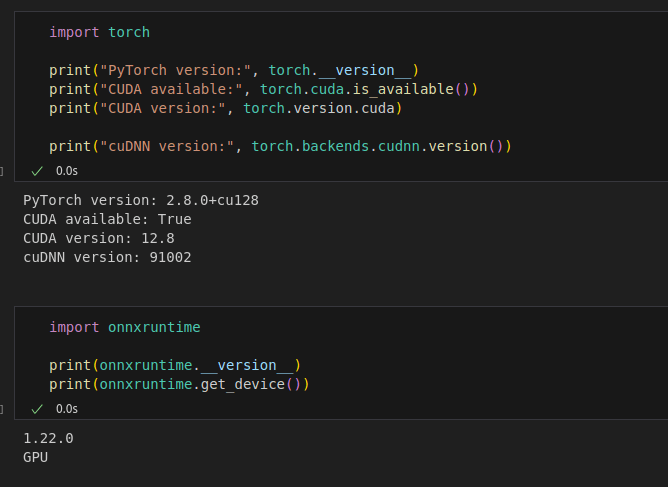
If you want to run models on GPU, you need to have Nvidia GPU on your computer. You need to install CUDA, and after that you can install onnx runtime with GPU support.
My environment:
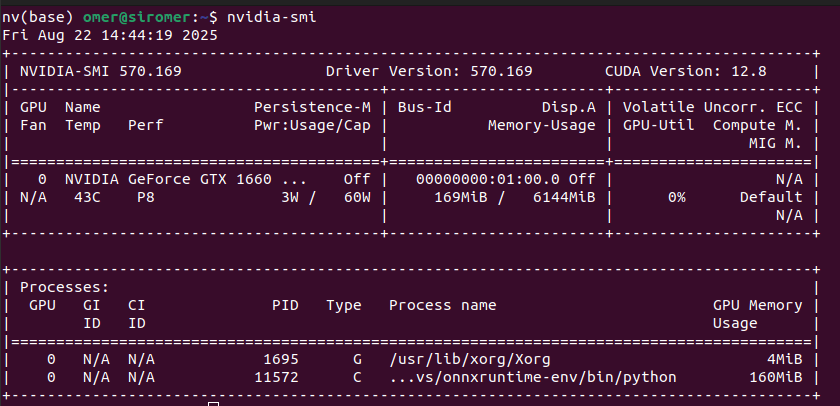
You need to find the appropriate CUDA version for your GPU. You can follow this Nvidia documentation. Trust me, there is nothing complex, just follow the documentation and pay attention to the versions.
If you can’t figure out which versions you need, you can even ask GPT. If you provide your GPU name, it can help you with the versions.
After you have installed CUDA on your system, it is time to install ONNX Runtime. You can’t directly install ONNX Runtime with pip, because specific versions must be installed for different CUDA versions. Check the image below.

I have CUDA 12.8, and I installed ONNX Runtime as shown below:
pip install onnxruntime-gpu>=1.19
If you don’t have a GPU, or if you want to use your CPU, you can install it directly as shown below:
pip install onnxruntime
Now, it is time for coding. There will be 3 different sections:
Before starting, as the name suggests, the first step will be to export the model to the ONNX format.
You can directly find the YOLO model in ONNX format on the internet, but I will use Ultralytics for model conversion. You can download class list(coco-labels-paper.txt) from this link.
from ultralytics import YOLO
# pretrained YOLOv8 model
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
# Export the model to ONNX format
model.export(format='onnx')
import onnxruntime as ort
import cv2
import numpy as np
import time
# Load ONNX model
session = ort.InferenceSession("models/yolov8n.onnx", providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider'])
input_name = session.get_inputs()[0].name
# Read video
video_path = "videos/street1.mp4"
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
# get width and height
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
# FPS calculation variables
fps_counter = 0
fps_start_time = time.time()
fps_display = 0.0
# Load COCO class names from file
with open('videos/coco-labels-paper.txt', 'r') as f:
class_names = [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()]
def postprocess_yolo_output(outputs, original_shape, conf_threshold=0.3, iou_threshold=0.45):
"""Post-process YOLOv8 ONNX output"""
predictions = outputs[0] # Shape: [1, 84, 8400]
predictions = predictions[0] # Remove batch dimension: [84, 8400]
predictions = predictions.T # Transpose to [8400, 84]
# Extract boxes and scores
boxes = predictions[:, :4] # First 4 columns are bbox coordinates
scores = predictions[:, 4:] # Remaining columns are class scores
# Get the class with highest score for each detection
class_ids = np.argmax(scores, axis=1)
confidences = np.max(scores, axis=1)
# Filter by confidence threshold
valid_detections = confidences > conf_threshold
boxes = boxes[valid_detections]
confidences = confidences[valid_detections]
class_ids = class_ids[valid_detections]
# Convert from center format to corner format
x_center, y_center, width, height = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 3]
x1 = x_center - width / 2
y1 = y_center - height / 2
x2 = x_center + width / 2
y2 = y_center + height / 2
boxes = np.column_stack((x1, y1, x2, y2))
# Scale boxes to original image size
orig_h, orig_w = original_shape[:2]
boxes[:, [0, 2]] *= orig_w / 640 # Scale x coordinates
boxes[:, [1, 3]] *= orig_h / 640 # Scale y coordinates
# Apply Non-Maximum Suppression to eliminate duplicate detections
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes.tolist(), confidences.tolist(), conf_threshold, iou_threshold)
# Check if any boxes remain after NMS
if len(indices) > 0:
indices = indices.flatten()
return boxes[indices], confidences[indices], class_ids[indices]
else:
return [], [], []
# Process video frames
while cap.isOpened():
frame_start_time = time.time()
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# YOLOv8 preprocessing
img = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img_resized = cv2.resize(img, (640, 640))
img_resized = img_resized.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
img_resized = np.transpose(img_resized, (2, 0, 1)) # HWC -> CHW
img_resized = np.expand_dims(img_resized, axis=0)
# Run inference
outputs = session.run(None, {input_name: img_resized})
# Post-process outputs
boxes, confidences, class_ids = postprocess_yolo_output(outputs, frame.shape)
# Draw detections
for box, conf, cls_id in zip(boxes, confidences, class_ids):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, box)
# Draw bounding box
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Draw label
label = f"{class_names[cls_id]}: {conf:.2f}"
label_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)[0]
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1 - label_size[1] - 10),
(x1 + label_size[0], y1), (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv2.putText(frame, label, (x1, y1 - 5),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1)
# Add title (optional)
title_text = "YOLOv8 Object Detection"
title_font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
title_scale = 1.0
title_thickness = 2
title_size = cv2.getTextSize(title_text, title_font, title_scale, title_thickness)[0]
title_x = (width - title_size[0]) // 2
title_y = 40
# Draw background rectangle for title
cv2.rectangle(frame, (title_x - 10, title_y - title_size[1] - 10),
(title_x + title_size[0] + 10, title_y + 10), (0, 0, 0), -1)
# Draw title text
cv2.putText(frame, title_text, (title_x, title_y), title_font, title_scale, (255, 255, 255), title_thickness)
# Calculate and display FPS
fps_counter += 1
if fps_counter % 10 == 0: # Update FPS display every 10 frames
fps_end_time = time.time()
fps_display = 10 / (fps_end_time - fps_start_time)
fps_start_time = fps_end_time
# Draw FPS
fps_text = f"FPS: {fps_display:.1f}"
cv2.rectangle(frame, (5, height - 40), (120, height - 10), (0, 0, 0), -1)
cv2.putText(frame, fps_text, (10, height - 20), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# --- 10. Display ---
cv2.imshow("YOLOv8 ONNX Runtime GPU", frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# Release everything
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
I had an article about training custom YOLO models, you can read it.
Export the ONNX model for the pretrained Faster R-CNN model. I will use PyTorch for exporting, but of course, you can directly find the ONNX model on the internet.
import torch
import torchvision
model = torchvision.models.detection.fasterrcnn_resnet50_fpn(pretrained=True)
model.eval()
dummy = torch.randn(1, 3, 800, 800) # typical input size
# Export the model
torch.onnx.export(model, dummy, "fasterrcnn.onnx",
opset_version=11,
input_names=["images"],
output_names=["boxes", "labels", "scores"])
import onnxruntime as ort
import cv2
import numpy as np
import time
# Check available providers first
print("Available ONNX Runtime providers:", ort.get_available_providers())
print("CUDA provider available:", 'CUDAExecutionProvider' in ort.get_available_providers())
# Load pretrained Faster R-CNN model
session = ort.InferenceSession("models/fasterrcnn.onnx", providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider'])
# Verify which providers are actually being used
print("Session providers:", session.get_providers())
print("Using GPU:", 'CUDAExecutionProvider' in session.get_providers())
# Check input/output details
input_details = session.get_inputs()[0]
print(f"\nInput name: {input_details.name}")
print(f"Input shape: {input_details.shape}")
print(f"Input type: {input_details.type}")
for i, output in enumerate(session.get_outputs()):
print(f"Output {i}: {output.name}, shape: {output.shape}")
# Load COCO class names from file (includes __background__ class for Faster R-CNN)
with open('videos/coco-labels-fasterrcnn.txt', 'r') as f:
coco_classes = [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()]
def preprocess_frame(frame, target_size=(800, 800)):
"""Preprocess frame for Faster R-CNN"""
# Convert BGR to RGB
rgb_frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Resize image
resized = cv2.resize(rgb_frame, target_size)
# Normalize to [0, 1]
normalized = resized.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
# Convert HWC to CHW
chw = np.transpose(normalized, (2, 0, 1))
# Add batch dimension
batch = np.expand_dims(chw, axis=0)
return batch
def postprocess_detections(outputs, original_shape, conf_threshold=0.5):
"""Post-process Faster R-CNN outputs"""
# Faster R-CNN typically outputs: boxes, labels, scores
# The exact order depends on how the model was exported
if len(outputs) == 3:
boxes, labels, scores = outputs
else:
# If single output, it might be a dictionary-like structure
# We'll need to adapt based on actual output format
print(f"Unexpected number of outputs: {len(outputs)}")
return [], [], []
# Remove batch dimension if present
if len(boxes.shape) == 3:
boxes = boxes[0]
if len(labels.shape) == 2:
labels = labels[0]
if len(scores.shape) == 2:
scores = scores[0]
# Filter by confidence threshold
valid_indices = scores > conf_threshold
filtered_boxes = boxes[valid_indices]
filtered_labels = labels[valid_indices]
filtered_scores = scores[valid_indices]
# Scale boxes to original image size
orig_h, orig_w = original_shape[:2]
if len(filtered_boxes) > 0:
# Boxes are typically in format [x1, y1, x2, y2] and normalized to [0, 800]
filtered_boxes[:, [0, 2]] *= orig_w / 800 # Scale x coordinates
filtered_boxes[:, [1, 3]] *= orig_h / 800 # Scale y coordinates
return filtered_boxes, filtered_labels, filtered_scores
# --- 2. Open video ---
video_path = "videos/street1.mp4"
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
# FPS calculation variables
fps_counter = 0
fps_start_time = time.time()
fps_display = 0.0
# Determine device string for display
device_str = "GPU" if 'CUDAExecutionProvider' in session.get_providers() else "CPU"
print(f"\nRunning Faster R-CNN with ONNX Runtime on {device_str}...")
print("Press 'q' to quit the video display")
# Loop through video frames
while cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# Preprocess frame
input_tensor = preprocess_frame(frame)
# Run inference
try:
outputs = session.run(None, {input_details.name: input_tensor})
# Post-process
boxes, labels, scores = postprocess_detections(outputs, frame.shape)
# Draw detections
for box, label, score in zip(boxes, labels, scores):
if len(box) >= 4:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, box[:4])
# Draw bounding box
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Draw label
class_name = coco_classes[int(label)] if int(label) < len(coco_classes) else f"class_{int(label)}"
label_text = f"{class_name}: {score:.2f}"
label_size = cv2.getTextSize(label_text, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)[0]
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1 - label_size[1] - 10),
(x1 + label_size[0], y1), (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv2.putText(frame, label_text, (x1, y1 - 5),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Inference error: {e}")
# Continue with next frame even if inference fails
# Calculate and display FPS
fps_counter += 1
if fps_counter % 10 == 0: # Update FPS display every 10 frames
fps_end_time = time.time()
fps_display = 10 / (fps_end_time - fps_start_time)
fps_start_time = fps_end_time
# Draw FPS with device info
fps_text = f"FPS: {fps_display:.1f} (Faster R-CNN-{device_str})"
cv2.rectangle(frame, (5, 5), (250, 35), (0, 0, 0), -1)
cv2.putText(frame, fps_text, (10, 25), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Display
cv2.imshow("Faster R-CNN ONNX Runtime", frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("Video processing completed!")
I had an article about training custom Faster R-CNN models, you can read it.
There are different ResNet image classification models. You can download the models from this link. You can also download the label list as shown below:
!wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/deep-learning-models/image-models/imagenet_class_index.json
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
import cv2
import json
# Load ONNX model
session = ort.InferenceSession("models/resnet50_Opset17.onnx", providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider'])
# Load ImageNet class labels
with open("imagenet_class_index.json") as f:
class_idx = json.load(f)
# Preprocess image
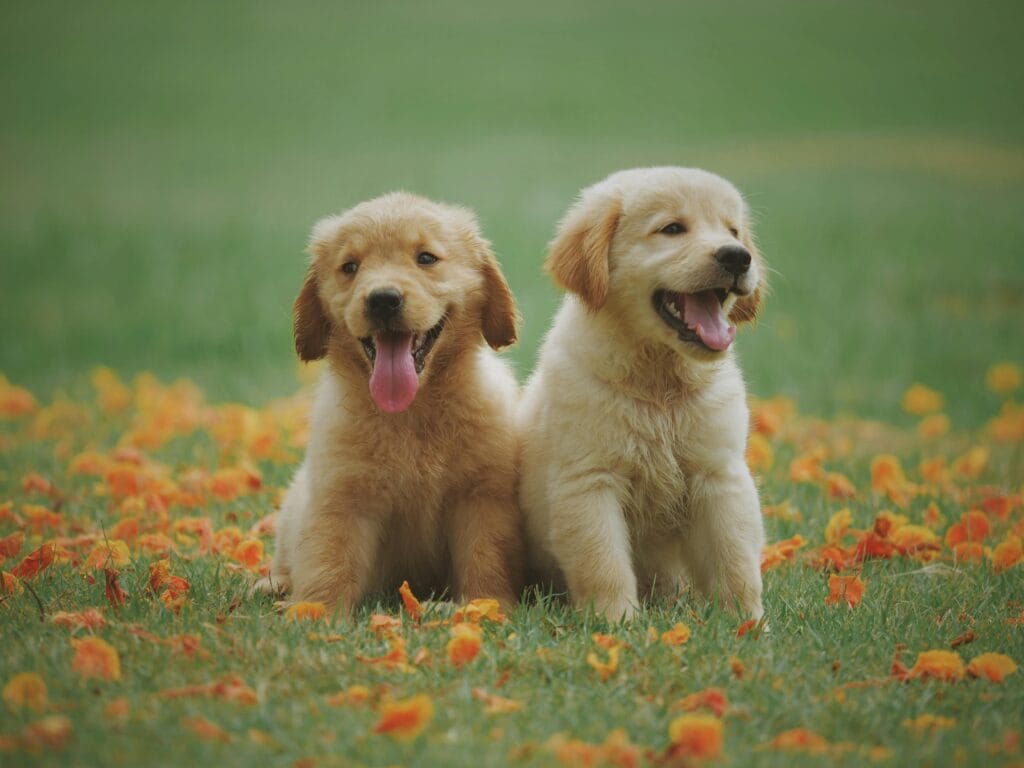
img = cv2.imread("videos/cat.jpg") # Your image path
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = cv2.resize(img, (224, 224))
img = img.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
# Normalize using ImageNet mean/std
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], dtype=np.float32)
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225], dtype=np.float32)
img = (img - mean) / std
# HWC -> CHW
img = np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1))
img = np.expand_dims(img, 0) # Add batch dimension
# Run inference
input_name = session.get_inputs()[0].name
outputs = session.run(None, {input_name: img})
# Postprocess
logits = outputs[0][0] # [1000]
# Apply softmax to get probabilities
probs = np.exp(logits) / np.sum(np.exp(logits))
# Get top-1 class
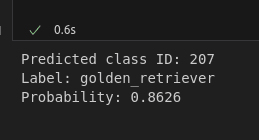
class_id = np.argmax(probs)
confidence = probs[class_id]
label = class_idx[str(class_id)][1] # e.g., "golden_retriever"
print(f"Predicted class ID: {class_id}")
print(f"Label: {label}")
print(f"Probability: {confidence:.4f}")