Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
→ YOLO Object Detection GUI that allows users to choose specific detection areas, labels, and adjust confidence values dynamically.
With libraries like Ultralytics, training a basic YOLO object detection model is no longer a complex task. By following a basic pipeline, it can be done in a few hours. This article is not about training a model; it is more about using the model efficiently after training. I will create a GUI that allows users to choose the detection area and specific labels, and you can improve this GUI and create a professional GUI that you can use in your projects or work.
I have a whole article dedicated to training a YOLO object detection model with custom datasets, and you can read it from here.
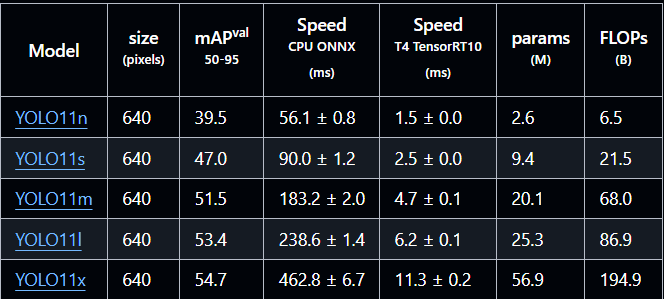
Now, I will use a pretrained YOLO model. You can use your own trained YOLO models or download pretrained models from Ultralytics GitHub repository.
There are a few key features of this GUI:
Now, I will explain small code snippets about these features, for the whole code you can directly go to the bottom of the page.
# Check if center is inside the polygon
if polygon_points:
distance = cv2.pointPolygonTest(polygon_pts, center, False)
if distance >= 0:
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, label, (x2, y1 - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255, 255, 0), 2)
# selected_labels are labels that user choiced
if label in selected_labels and conf >= conf_threshold:
......
# Check if center is inside the polygon
if polygon_points:
......
To draw a polygon, use the left mouse button. To complete the polygon, use the right mouse button. You can clear the screen by pressing the ‘c’ key.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
import numpy as np
# Load the YOLO model
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
# Label dictionary
label_dict = {0: 'person', 1: 'bicycle', 2: 'car', 3: 'motorcycle', 4: 'airplane', 5: 'bus', 6: 'train', 7: 'truck', 8: 'boat', 9: 'traffic light', 10: 'fire hydrant', 11: 'stop sign',
12: 'parking meter', 13: 'bench', 14: 'bird', 15: 'cat', 16: 'dog', 17: 'horse', 18: 'sheep', 19: 'cow', 20: 'elephant', 21: 'bear', 22: 'zebra', 23: 'giraffe', 24: 'backpack', 25: 'umbrella', 26: 'handbag', 27: 'tie', 28: 'suitcase', 29: 'frisbee', 30: 'skis', 31: 'snowboard', 32: 'sports ball', 33: 'kite', 34: 'baseball bat', 35: 'baseball glove', 36: 'skateboard', 37: 'surfboard', 38: 'tennis racket', 39: 'bottle', 40: 'wine glass', 41: 'cup', 42: 'fork', 43: 'knife', 44: 'spoon', 45: 'bowl', 46: 'banana', 47: 'apple', 48: 'sandwich', 49: 'orange', 50: 'broccoli', 51: 'carrot', 52: 'hot dog', 53: 'pizza', 54: 'donut', 55: 'cake', 56: 'chair', 57: 'couch', 58: 'potted plant', 59: 'bed', 60: 'dining table', 61: 'toilet', 62: 'tv', 63: 'laptop', 64: 'mouse', 65: 'remote', 66: 'keyboard', 67: 'cell phone', 68: 'microwave', 69: 'oven', 70: 'toaster', 71: 'sink', 72: 'refrigerator', 73: 'book', 74: 'clock', 75: 'vase', 76: 'scissors', 77: 'teddy bear', 78: 'hair drier', 79: 'toothbrush'}
# Initialize the main application window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("YOLO Video Detection")
# Create a frame for the video display
video_frame = tk.Frame(root, width=600, height=400)
video_frame.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10, pady=10)
# Create a label for the video feed
video_label = tk.Label(video_frame)
video_label.pack()
# Create a frame for label selection and confidence score slider
control_frame = tk.Frame(root)
control_frame.pack(side=tk.RIGHT, padx=10, pady=30, fill=tk.Y)
confidence_slider = tk.Scale(control_frame, from_=0, to_=100, orient=tk.HORIZONTAL, length=200, label="Confidence")
confidence_slider.set(10) # Default value for confidence
confidence_slider.pack(pady=10)
# Create a canvas for scrollable label selection
label_canvas = tk.Canvas(control_frame)
label_canvas.pack(side=tk.LEFT, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
scrollbar = tk.Scrollbar(control_frame, orient="vertical", command=label_canvas.yview)
scrollbar.pack(side=tk.RIGHT, fill="y", pady=20)
label_canvas.configure(yscrollcommand=scrollbar.set)
label_canvas.bind('<Configure>', lambda e: label_canvas.configure(scrollregion=label_canvas.bbox("all")))
label_inner_frame = tk.Frame(label_canvas)
label_canvas.create_window((0, 0), window=label_inner_frame, anchor="nw")
# Add a label for instruction
label_text = tk.Label(label_inner_frame, text="Select Labels to Detect:")
label_text.pack()
# Add checkboxes for each label
label_vars = {label: tk.BooleanVar(value=True) for label in label_dict.values()}
for label in label_dict.values():
chk = tk.Checkbutton(label_inner_frame, text=label, var=label_vars[label])
chk.pack(anchor=tk.W)
# List to store polygon points
polygon_points = []
def process_video():
# Define maximum width and height
max_width = 600
max_height = 400
# Open video capture (0 for webcam)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("room-video.mp4")
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# Resize frame if it exceeds maximum width or height
height, width = frame.shape[:2]
if width > max_width or height > max_height:
# Calculate scaling factor
scale = min(max_width / width, max_height / height)
new_width = int(width * scale)
new_height = int(height * scale)
frame = cv2.resize(frame, (new_width, new_height))
# Get selected labels
selected_labels = [label for label, var in label_vars.items() if var.get()]
# Get confidence score from slider
conf_threshold = confidence_slider.get() / 100.0
# Run YOLO detection
results = model(frame)
# Convert polygon points to OpenCV coordinates
if polygon_points:
polygon_pts = np.array([(x, y) for x, y in polygon_points], np.int32)
polygon_pts = polygon_pts.reshape((-1, 1, 2))
# Filter results based on selected labels and confidence score
for result in results:
for id, box in enumerate(result.boxes.xyxy):
class_id = int(result.boxes.cls[id])
label = label_dict[class_id]
conf = result.boxes.conf[id]
if label in selected_labels and conf >= conf_threshold:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, box)
center = ((x1 + x2) // 2, (y1 + y2) // 2)
# Check if center is inside the polygon
if polygon_points:
distance = cv2.pointPolygonTest(polygon_pts, center, False)
if distance >= 0:
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, label, (x2, y1 - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255, 255, 0), 2)
# Draw the polygon on the frame if there are points
if len(polygon_points) > 1:
pts = np.array(polygon_points, np.int32)
pts = pts.reshape((-1, 1, 2))
cv2.polylines(frame, [pts], isClosed=True, color=(0, 255, 0), thickness=2)
# Convert the image to a format Tkinter can display
frame_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = Image.fromarray(frame_rgb)
imgtk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(image=img)
video_label.imgtk = imgtk
video_label.configure(image=imgtk)
root.update()
def on_mouse_click(event):
global polygon_points
if event.num == 1: # Left click
# Add point to polygon points list
polygon_points.append((event.x, event.y))
elif event.num == 3: # Right click
# Draw polygon with all collected points and clear points list
if len(polygon_points) > 1:
video_label.delete("polygon") # Clear any previous drawings
pts = np.array(polygon_points, np.int32)
pts = pts.reshape((-1, 1, 2))
video_label.create_polygon(pts.tolist(), outline="green", fill="", width=2, tags="polygon")
polygon_points = [] # Clear points list after drawing
def clear_polygon(event):
global polygon_points
polygon_points = []
video_label.delete("polygon") # Clear any previous drawings
# Bind mouse click events to the video label
video_label.bind("<Button-1>", on_mouse_click) # Left mouse click
video_label.bind("<Button-3>", on_mouse_click) # Right mouse click
# Bind the "c" key to the clear_polygon function
root.bind("c", clear_polygon)
# Start the video processing in the main loop
root.after(0, process_video)
# Run the GUI loop
root.mainloop()