Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
→ Perform object detection on multiple streams with YOLO models on Jetson devices and NVIDIA GPUs.
Object detection with multiple streams is important for tasks like security cameras, traffic management, industrial automation, monitoring people, and more. Object detection is a computationally expensive task, therefore optimization of resources is important for applications. NVIDIA DeepStream SDK is powerful for AI tasks and is perfectly optimized by NVIDIA engineers.
In this article, I will show you how to perform detection with a custom YOLO model on multiple streams using the DeepStream SDK. Depending on your GPU, you can perform detection on more than 30 videos simultaneously.
You have two options to use Deepstream SDK :
I have an Ubuntu 22.04 operating system, but steps are same for different devices and ubuntu versions.
This part might be a little boring and relatively long, but if you follow the links and steps one by one, everything will be simple and clear.
After the first step, you can run demo models by following the documentation, but you can’t directly run YOLO models. You need some kind of bridge for detection with YOLO models.
You just need to be careful about versions. If you follow the links, you won’t have any problems with the versions.
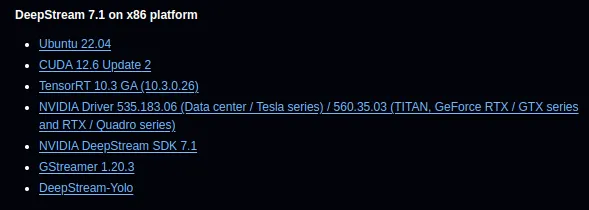
I will use a pretrained YOLOv8 model(yolov8s.pt), but you can use your custom YOLO models; steps are same. The DeepStream-Yolo repository supports different versions of YOLO. There are config files for each supported model, and don’t worry, I will show you how to modify these config files.
If you want to learn more about training custom YOLO models, you can read my article.
You can download a pretrained YOLOv8 model from here. Now, it is time to use the YOLO model with DeepStream.
We can’t directly use YOLO models, we need to convert them to ONNX models. Luckily, there is a Python script inside DeepStream-Yolo repository. Go inside the utils folder and copy your YOLO model there.
Inside the utils folder, there are Python files for conversion. Look at the image below.
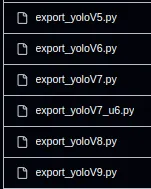
Now it is time for conversion. I will use export_yoloV8.py. There are different parameters, and you can check these parameters for adjusting your model (link) , but it will work like this as well:
/DeepStream-Yolo/utils$ python3 export_yoloV8.py -w yolov8s.pt — dynamic — simplify
Now copy your ONNX file to the DeepStream-Yolo folder.
DeepStream has different demo applications for various tasks. I will use deepstream-app, it supports multiple streams. It’s better to use demo applications for a while because writing a DeepStream application from scratch is a complex task.
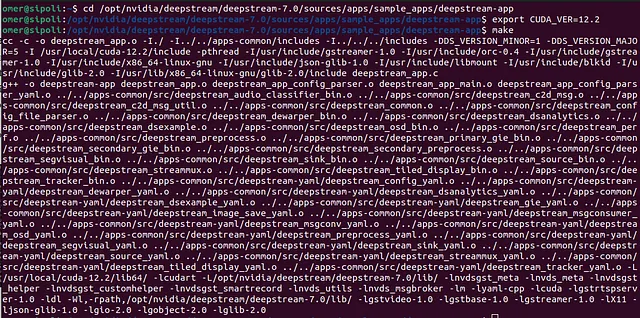
Now, let’s compile the deepstream-app. First, go to the deepstream-app folder, then export the CUDA version, and finally compile it. Look at the image below.
After this step, we are going to run our models. There are two different configuration files that we need.
There are hundreds of parameters, I will only talk about most important ones (documentation).
Inside deepstream_app_config.txt :
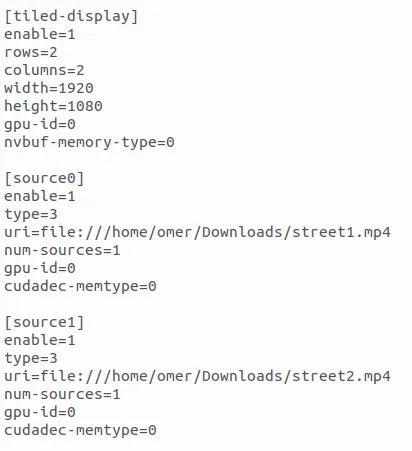
config_infer_primary_yoloV8.txt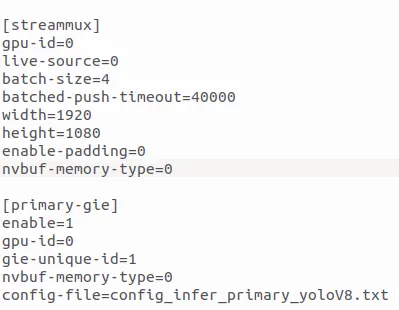
Inside config_infer_primary_yoloV8.txt :
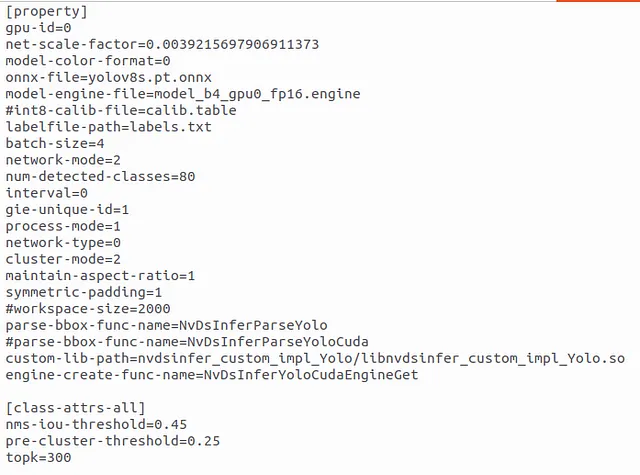
Everything is ready, it is time for object detection. First time it will take some time to create files(15-20 minutes).
Navigate to the DeepStream-Yolo folder and run the DeepStream application using the following command:
/opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream/7.0/sources/apps/sample_apps/deepstream-app/deepstream-app -c deepstream_app_config.txtDont forget to change version deepstream/7.0
Here, we are using the already compiled deepstream-app (Step 2) and our config file (Step 3). Look at the FPS values; even with my old GPU (GTX 1660 Ti), the FPS values are really good.